Our Blog
Blog
What Are Air Ducts? The Homeowner’s Guide To HVAC Ductwork

By: Statewide Heating

Wednesday, May 8, 2024
Are you puzzled by the maze of ducts that weave through your home? Understanding the intricacies of air ducts can dramatically improve the efficiency of your heating system, especially if you're relying on a Forced Air System or gas furnace. Air ducts are not just passages for moving air; they are the lifelines of your home's HVAC system, influencing everything from your comfort to your energy bills.
This guide will explore how air ducts function, why they are essential for your heating system, and how they work in tandem with your gas furnace to deliver optimal home comfort. Learn to navigate the complexities of HVAC ductwork, and take control of your home’s climate—knowledge is power when it comes to maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient living environment.
How Much Does Furnace Installation Cost?
Before diving into the costs of furnace installation, it's essential to understand the value it brings. A new furnace not only enhances the energy efficiency of your home by optimizing the use of thermal energy but also modernizes your air systems for superior climate control and reduced energy expenditures.
Mechanism of Forced Convection
Forced convection is a key mechanism in HVAC systems, particularly in Forced Air Heating. This process uses fans or blowers to distribute heat air efficiently throughout your home, ensuring consistent temperatures in all rooms.
By actively circulating air, forced convection maximizes the reach and effectiveness of your heating system. This ensures that thermal energy is evenly distributed by your air systems, avoiding cold spots and enhancing overall comfort.
The advantage of forced convection lies in its ability to speed up the heating process. Air systems that employ this method can quickly adjust the temperature of the air as it passes through the heat exchanger, improving the system's response time and energy efficiency.
What Is HVAC?
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It's an integrated system that ensures your indoor environment remains comfortable and healthy by regulating temperature, airflow, and humidity levels.
An HVAC system is not just about warming or cooling spaces; it also involves cleaning the air and maintaining optimal humidity. This multi-faceted approach ensures that your living or working environment is always conducive to well-being and comfort.
Understanding how HVAC systems operate can help homeowners make informed decisions about upgrades and maintenance. Whether it's Forced Air Heating or other forms, each component works to efficiently manage the thermal energy within your home.
Understanding the Efficiency Rating of Furnaces and Boilers
The efficiency of furnaces and boilers is often rated by the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) percentage. This rating indicates how well the appliance converts energy from its fuel to heat air over a typical year.
Higher efficiency ratings in furnaces and boilers mean lower fuel costs and reduced environmental impact. An efficient system maximizes the thermal energy produced, cutting down on waste and excess expenses.
When selecting a new heating system, considering the efficiency rating is crucial. A higher rating implies that your air systems are not only cost-effective but also contribute to a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with modern energy standards.
Replacing Your Furnace or Boiler
Replacing an outdated furnace or boiler can significantly improve your home’s air conditioning efficiency. A new system with a high AFUE rating and a second heat exchanger utilizes fuel more effectively, enhancing your system's energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Consider the long-term savings when replacing your heating unit. Modern furnaces and boilers are designed to optimize air conditioning and heating efficiency, thanks to advancements like the second heat exchanger, which recycles exhaust gases to extract additional heat.
The decision to replace should also factor in the age and repair history of your existing unit. Upgrading to a more energy-efficient model can prevent frequent breakdowns and maintain consistent air conditioning performance, ensuring your home remains comfortable year-round.
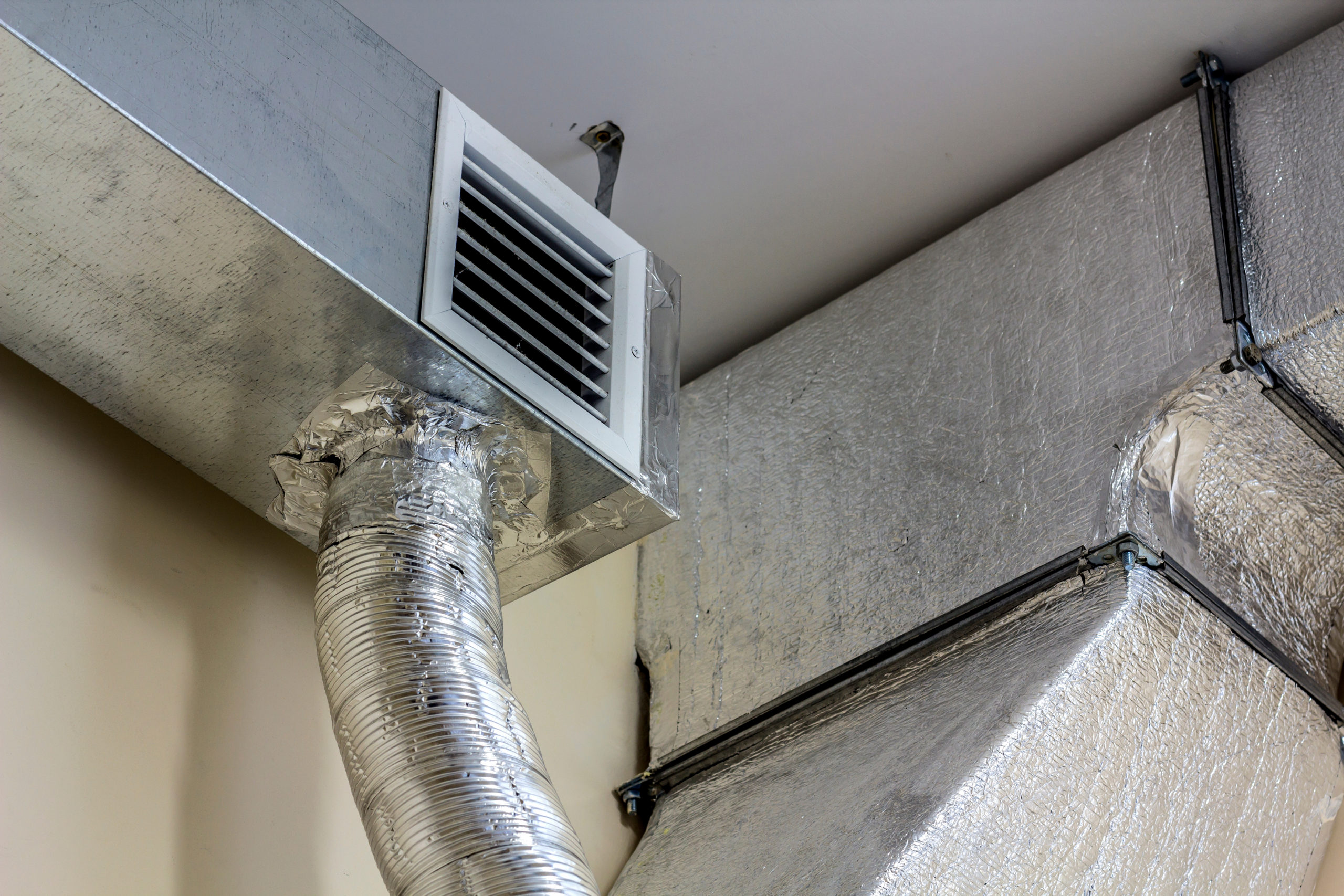
Sheet Metal Duct
Sheet metal ducts are a durable and efficient option for guiding air throughout your home’s air conditioning system. Their smooth interior surfaces allow for minimal resistance, maximizing the system's energy efficiency by facilitating optimal airflow.
When installing or upgrading ductwork, consider sheet metal for its longevity and ability to maintain a clean air path. This minimizes the energy lost and enhances the overall efficiency of your air conditioning and heating systems.
Properly sealed and insulated sheet metal ducts can prevent energy loss, ensuring that heated or cooled air reaches its intended destinations without temperature fluctuations. This stability is crucial for maintaining the system’s energy efficiency and providing consistent comfort.
Gravity Air Furnace Systems
Gravity air furnace systems utilize natural principles for air movement, eliminating the need for blowers. Warm air rises through ducts by natural convection, providing a silent method of heating without the complexity of a second heat exchanger.
These systems are less common today but offer simplicity and lower initial costs compared to forced-air systems. They rely on the natural movement of warm air to distribute heat, which can be ideal for homes with specific architectural constraints.
While gravity systems are inherently less efficient than modern forced air systems with a second heat exchanger, they can be a suitable option for homes where noise levels and energy use from additional mechanical components are a concern. Always assess the compatibility with your overall air conditioning needs before installation.
Other Potential Cost Factors to Consider
When planning for HVAC upgrades or installations, consider costs beyond the equipment itself. HVAC contractors often charge for additional services like ductwork modification or electrical upgrades, which can significantly impact your budget.
Don't overlook the potential for local or federal energy rebates which can offset installation costs. Consulting with knowledgeable HVAC contractors can help you identify these opportunities, maximizing your investment in efficient systems.
Long-term operational costs, such as increased energy use or maintenance fees, should also be factored in. Efficient systems like heat pumps might have higher upfront costs but typically offer lower monthly expenses through improved energy use.
Traditional Boiler and Radiator Systems
Traditional boiler and radiator systems circulate heated air through large, visible radiators. These systems are known for their ability to maintain steady heat levels and add a touch of classic aesthetic to any room.
The operation of boilers and radiators is relatively straightforward, making them a favorite for those seeking durability and ease of maintenance. However, they require regular checks and maintenance by skilled HVAC contractors to ensure peak performance.
While they are generally more expensive to install and run than modern heat pumps, traditional systems are often ideal for homes in colder climates due to their effectiveness in maintaining a constant heat supply.
10 Types of Home Heating Systems and How to Choose One
From furnaces and heat pumps to boilers and radiant floors, the options for home heating systems are diverse. Each type offers unique benefits, such as the efficiency of heat pumps or the comfortable heat of radiant floors.
When choosing a heating system, consider the climate, house layout, and energy costs. Heat pumps, for example, are excellent in moderate climates but might not perform well in extreme cold without supplemental heating.
Consult with professional HVAC contractors to assess your home’s specific needs. They can provide insights into which system—from forced air to hybrid systems—will offer the best balance of comfort, cost-efficiency, and energy use.
In-Floor Radiant Heating Systems
In-floor radiant heating systems deliver a consistent level of warm air throughout your space by heating the floors directly. This system evenly distributes heated air, reducing cold spots and increasing comfort in living areas.
These systems are highly efficient as they heat objects and surfaces directly, rather than just the air, allowing for a lower overall temperature setting while maintaining comfort. The warmth radiates upwards, enveloping the room in gentle heat.
The installation of in-floor systems is more invasive and typically more expensive upfront, but they offer substantial long-term savings in energy costs. Their ability to maintain consistent warm air with minimal maintenance makes them an attractive option for many homeowners.
Hot Water Baseboard Radiator
Hot Water Baseboard Radiators operate by circulating hot water through pipes located along the baseboards of a room. This system efficiently heats the space, emitting a steady supply of warm air without the noise associated with forced-air systems.
The simplicity and effectiveness of hot water systems in maintaining a comfortable temperature make them a preferred choice for many. They are less likely to distribute allergens compared to systems that rely on forced air, promoting a healthier living environment.
While the initial setup for hot water baseboard radiators can be costly, their operational efficiency is higher. They provide a constant temperature, reducing the need for frequent adjustments and potentially lowering heating costs over time.
Furnace Unit Size
Choosing the correct furnace unit size is crucial for efficiency. An undersized unit will continuously run, struggling to heat the home and wear out prematurely. Conversely, an oversized unit cycles too frequently, reducing its efficiency and lifespan while failing to effectively distribute heated air.
The right size furnace optimizes energy usage by delivering consistent warm air throughout your home. This balance ensures that every corner of your space receives equal heating, enhancing overall comfort and system effectiveness.
Consulting with HVAC professionals to determine the appropriate size can prevent inefficiencies and future problems. They assess your home’s layout, insulation, and climate to recommend a unit that will operate at peak performance, ensuring your home is comfortably heated with optimal energy efficiency.
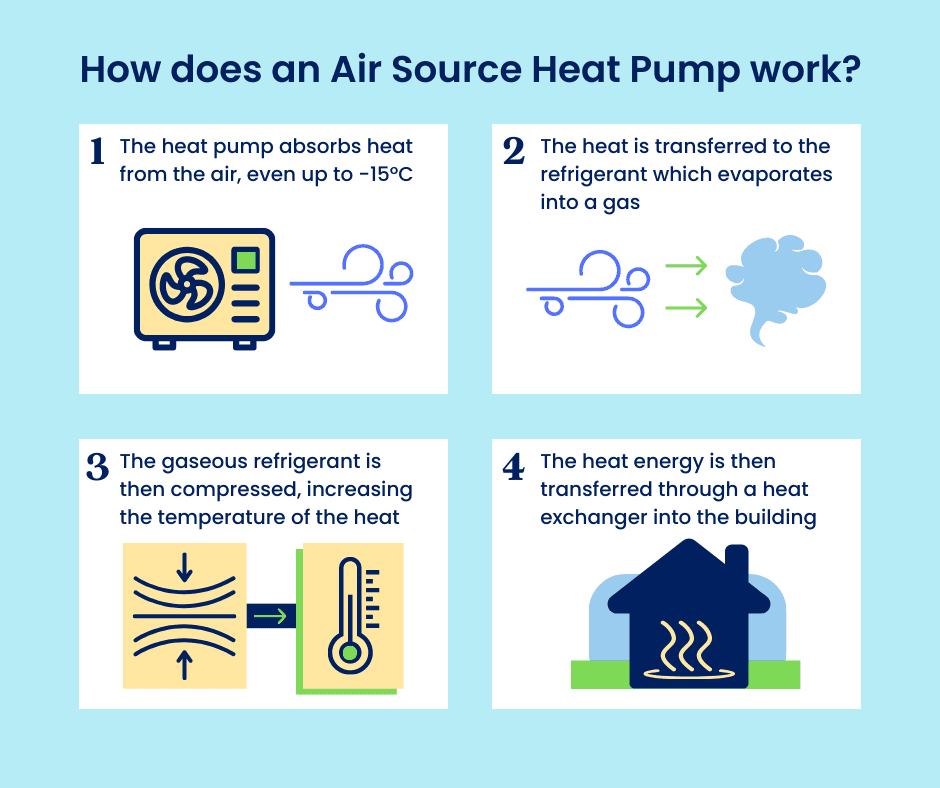
Heat Pump Heating Systems
Heat pump heating systems are versatile units that provide both warm and cool air, making them ideal for year-round climate control. Their ability to reverse operation allows them to function like an air conditioner in summer and a heater in winter.
These systems are particularly effective in areas with moderate climates and can significantly reduce electricity use compared to traditional heating methods like natural gas furnaces. Their efficiency stems from transferring heat rather than generating it.
Investing in a high efficiency furnace that includes a heat pump can be cost-effective in the long run. Heat pumps use less energy to operate, leading to lower utility bills and less environmental impact while maintaining comfortable temperatures.
How to Reduce Furnace Installation Costs?
One way to reduce the cost of furnace installation is to consider a high efficiency furnace that may qualify for energy rebates and tax incentives. These can substantially lower the upfront costs and improve long-term savings.
Scheduling installations during off-peak seasons can also lead to lower costs. Many HVAC contractors offer discounts in spring and fall when demand is lower, providing an opportunity to save on installation fees.
Consider retrofitting your existing system instead of a full replacement when possible. Upgrades like adding a second heat exchanger or improving ductwork can enhance the system's energy efficiency at a fraction of the cost of a new furnace.
Installation vs. Replacement
Installation of a new furnace system involves setting up a furnace in a home for the first time, which can be more complex and costly due to the need for new ductwork and other infrastructural elements.
Replacement, however, generally deals with swapping out an old furnace for a new one. It can be less expensive than a full installation, especially if the existing ductwork and infrastructure can be used.
Deciding between installation or replacement should consider the current system's age, efficiency, and repair history. While replacement of a less efficient system with a high efficiency furnace might seem costly upfront, the savings in energy costs and improved performance can justify the investment.
Low Indoor Air Quality
Low indoor air quality is often exacerbated by inadequate ventilation and old HVAC systems. Upgrading to a ductless mini-split system can enhance air quality by reducing the circulation of allergens and pollutants.
Regular maintenance and cleaning of HVAC systems, including the replacement of filters, are crucial for maintaining high indoor air quality. This prevents the accumulation of dust and mold, which can be harmful to health.
Investing in additional air purification systems can also significantly improve indoor air quality. These systems work in tandem with your existing HVAC to remove contaminants from the air, creating a healthier living environment.
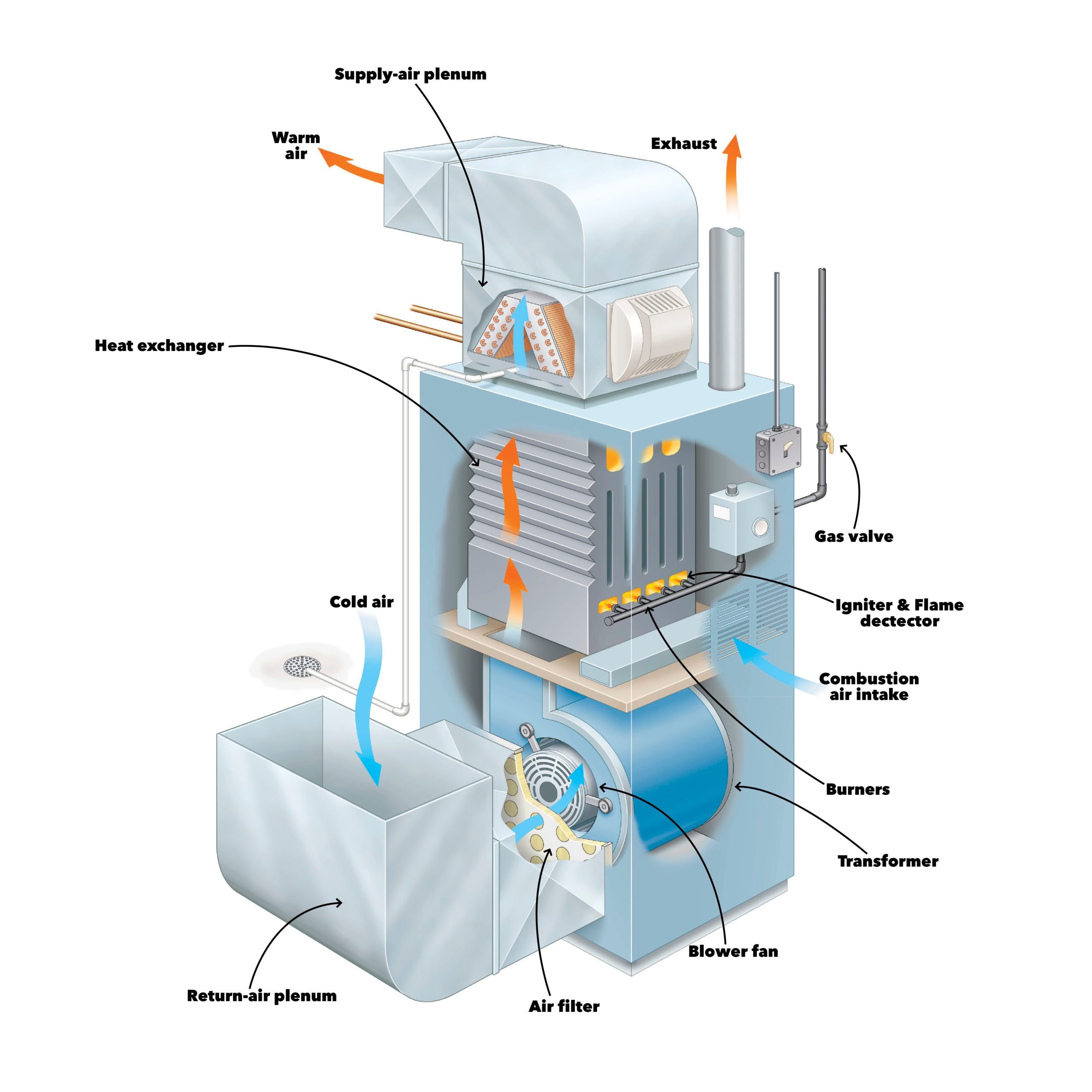
How Air Flows In A Forced Air Duct System
In a forced air duct system, air is heated or cooled by the HVAC unit and then pushed through a series of ducts by a blower. This efficient movement allows for consistent heating or cooling across different areas of the home.
The design of the ductwork, including its layout and size, plays a critical role in how effectively the air is distributed. Properly designed ductwork ensures even distribution of warm or cool air, preventing hot or cold spots.
To optimize the efficiency of a forced air system, ensuring that the ducts are well-sealed and insulated is crucial. This prevents the loss of heated or cooled air, maximizing the system’s energy efficiency and helping homeowners save money on utility bills.
Can I get tax credit for installing a new furnace?
Many governments offer tax credits to homeowners who install energy-efficient systems like high-efficiency furnaces. These incentives are designed to encourage the reduction of energy consumption and promote the use of sustainable technologies.
To qualify for these tax credits, the furnace typically needs to meet specific energy efficiency criteria set by governmental or environmental agencies. It's important to check the latest requirements and ensure that your new system complies.
Consulting with HVAC professionals or tax experts can help homeowners navigate the qualifications for these tax credits. They can provide detailed information on which systems qualify, how much you can save, and how to claim these benefits effectively.
HVAC Ductwork Installation Problems
One common issue during HVAC ductwork installation is improper sizing relative to the home's square footage. Ducts that are too small can restrict airflow, leading to inefficiencies and uneven heating or cooling at different temperatures throughout the house.
Leaks and poor sealing are other significant problems that can arise during ductwork installation. These issues result in energy loss, increased utility bills, and difficulty maintaining desired temperatures, especially in larger homes with extensive square footage.
Installation complications may also occur when integrating ductwork with older systems that previously used other heating methods, such as fuel oil. Adapting new ducts to work effectively with existing structures requires precise planning and execution.
How long does it take for a furnace to be installed?
The installation time for a new furnace largely depends on the complexity of the system and the specifics of the home’s layout. For standard replacements without extensive modifications, the process can typically be completed within a day.
However, if the installation involves converting from another type of heating system, such as fuel oil, or extensive ductwork adjustments are required, it may take several days to complete. This includes time for removing the old system and ensuring the new system is properly calibrated.
The size of the home and the furnace's capacity also play crucial roles. Larger homes with greater square footage may require more time to ensure that the system can efficiently handle different temperatures and provide uniform heating or cooling throughout the space.